Data :-Data can be analog or digital. Analog data are continuous and take continuous values. Digital data have discrete states and take discrete values.
signal:- A signal is an electrical or electromagnetic current that is used for carrying data from one device or network to another.
Signals can be analog or digital. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values in a range; digital signals can have only a limited number of values.
periodic signal:-A signal is a periodic signal if it completes a pattern within a measurable time frame, called a period and repeats that pattern over identical subsequent periods. The completion of a full pattern is called a cycle. A period is defined as the amount of time (expressed in seconds) required to complete one full cycle.
Non-periodic Signal. Definition: A signal is considered to be non-periodic or a periodic signal when it does not repeat its pattern over a period (i.e. interval of time).


note:- sine wave a curve representing periodic oscillations of constant amplitude as given by a sine function.
note:- amplitude :-the angular distance of a celestial object from the true east or west point of the horizon at rising or setting.

signal:- A signal is an electrical or electromagnetic current that is used for carrying data from one device or network to another.
Signals can be analog or digital. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values in a range; digital signals can have only a limited number of values.
periodic signal:-A signal is a periodic signal if it completes a pattern within a measurable time frame, called a period and repeats that pattern over identical subsequent periods. The completion of a full pattern is called a cycle. A period is defined as the amount of time (expressed in seconds) required to complete one full cycle.
Non-periodic Signal. Definition: A signal is considered to be non-periodic or a periodic signal when it does not repeat its pattern over a period (i.e. interval of time).
Analog Signal:-
An analog signal is a continuous wave denoted by a sine wave (pictured below) and may vary in signal strength (amplitude) or frequency (waves per unit time). The sine wave's amplitude value can be seen as the higher and lower points of the wave, while the frequency value is measured in the sine wave's physical length from left to right.
There are many examples of analog signals around us. The sound from a human voice is analog, because sound waves are continuous, as is our own vision, because we see various shapes and colors in a continuous manner due to light waves. Even a typical kitchen clock having its hands moving continuously can be represented as an analog signal.

Digital Signal
A digital signal - a must for computer processing - is described as using binary (0s and 1s), and therefore, cannot take on any fractional values. As illustrated in the graphic below, digital signals retain a uniform structure, providing a constant and consistent signal. Because of the inherent reliability of the digital signal, technology using it is rapidly replacing a large percentage of analog applications and devices.
For example, the wristwatch, showing the time of day, with its minute, hour, and sweeping second hands, is being replaced by the digital watch, which offers the time of day and other information using a numerical display. A typical digital signal is represented below. Note the equally dispersed 1s and 0s.

In data communications, we commonly use periodic analog signals
and non periodic digital signals.
Data Transmission
Periodic analog signals can be classified as simple or composite. A
simple periodic analog signal, a sine wave, cannot be decomposed
into simpler signals. A composite periodic analog signal is composed
of multiple sine waves.
note:- amplitude :-the angular distance of a celestial object from the true east or west point of the horizon at rising or setting.
Composite periodic Signal:-
A composite Signal Can be periodic or no periodic.
A periodic composite signal can be decomposed into a
series of simple sine waves with discrete frequencies –
Frequencies that have integer values (1,2,3, and so on).
A non-periodic composite signal can be decomposed
into a combination of an infinite number of simple sine waves with continuous frequencies,
frequencies that have real values.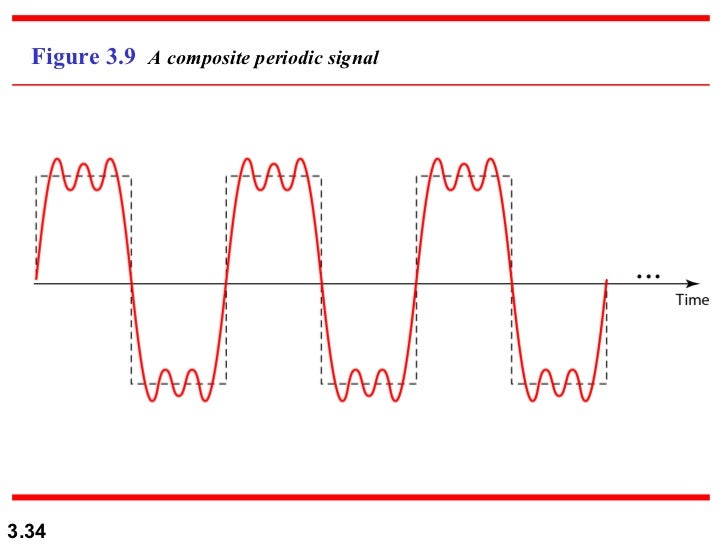

Data Communication | Transmission Impairment
In communication system, analog signals travel through transmission media, which tends to deteriorate the quality of analog signal. This imperfection causes signal impairment. This means that received signal is not same as the signal that was send.
Causes of impairment –

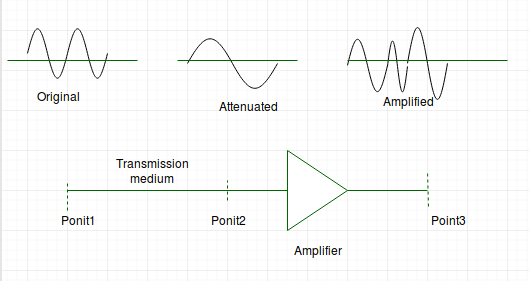
Attenuation – It means loss of energy. The strength of signal decreases with increasing distance which causes loss of energy in overcoming resistance of medium. This is also known as attenuated signal. Amplifiers are used to amplify the attenuated signal which gives the original signal back.

Attenuation is measured in decibels(dB). It measures the relative strengths of two signals or one signal at two different point.
Attenuation(dB) = 10log10(P2/P1)
P1 is power at sending end and P2 is power at receiving end.
- Distortion – It means change in the shape of signal. This is generally seen in composite signals with different frequencies. Each frequency component has its own propagation speed travelling through a medium. Every component arrive at different time which leads to delay distortion. Therefore, they have different phases at receiver end from what they had at senders end.
- Noise – The random or unwanted signal that mixes up with the original signal is called noise. There are several types of noise such as induced noise, crosstalk noise, thermal noise and impulse noise which may corrupt the signal.Induced noise comes from sources such as motors and appliances. These devices act as sending antenna and transmission medium act as receiving antenna. Thermal noise is movement of electrons in wire which creates an extra signal. Crosstalk noise is when one wire affects the other wire.
No comments:
Post a Comment